publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2025
-
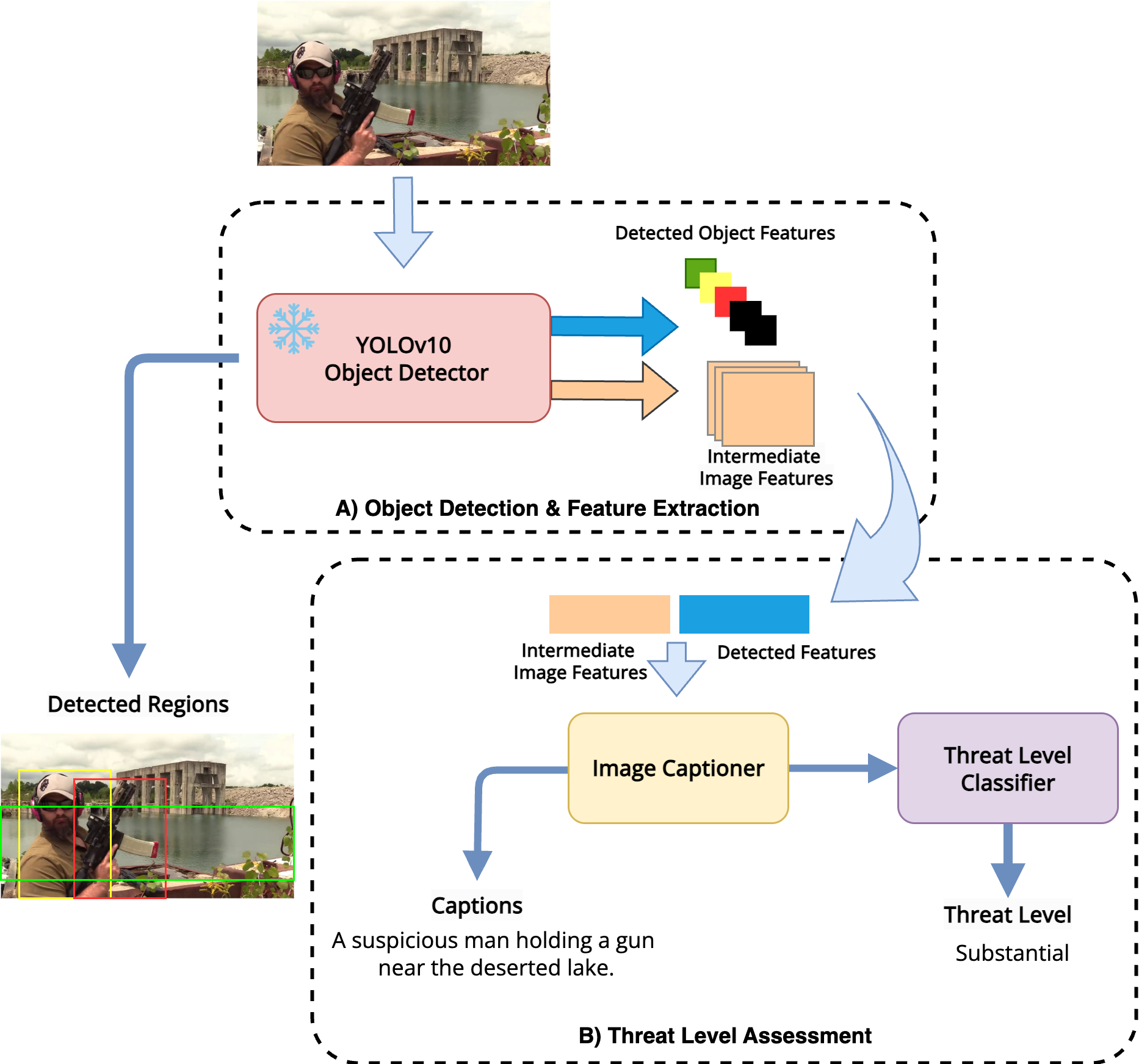 ThreatNet: Multimodal Firearm Threat Assessment Network (Accepted)Albert Mundu, Satish Kumar Singh, and Shiv Ram DubeyIEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, 2025
ThreatNet: Multimodal Firearm Threat Assessment Network (Accepted)Albert Mundu, Satish Kumar Singh, and Shiv Ram DubeyIEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, 2025Firearm-related violence poses a persistent threat to public safety, often challenging even law enforcement. In this paper, we introduce ThreatNet, a multimodal firearm threat assessment network that detects weapons in unconstrained environments and evaluates scene severity. ThreatNet integrates a YOLOv10-based object detector with a dual-branched transformer-based image captioner to generate descriptive scene narratives and classify threat levels. We present the YoutubeGDD caption dataset, an extension of YoutubeGDD, featuring real-world weapon images with five captions per image to support multimodal analysis. We finetune the pretrained detector on YoutubeGDD dataset for weapon recognition, while we train the captioner and threat classifier on both YoutubeGDD caption and MS-COCO caption datasets. We evaluate model performance using captioning metrics and threat classification accuracy, and benchmark YOLOv10 variants on YoutubeGDD dataset and our captioner on MS-COCO caption dataset.
@article{upcon25_threatnet, title = {ThreatNet: Multimodal Firearm Threat Assessment Network (Accepted)}, author = {Mundu, Albert and Kumar Singh, Satish and Ram Dubey, Shiv}, journal = {IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering}, year = {2025}, publisher = {IEEE}, }
2024
-
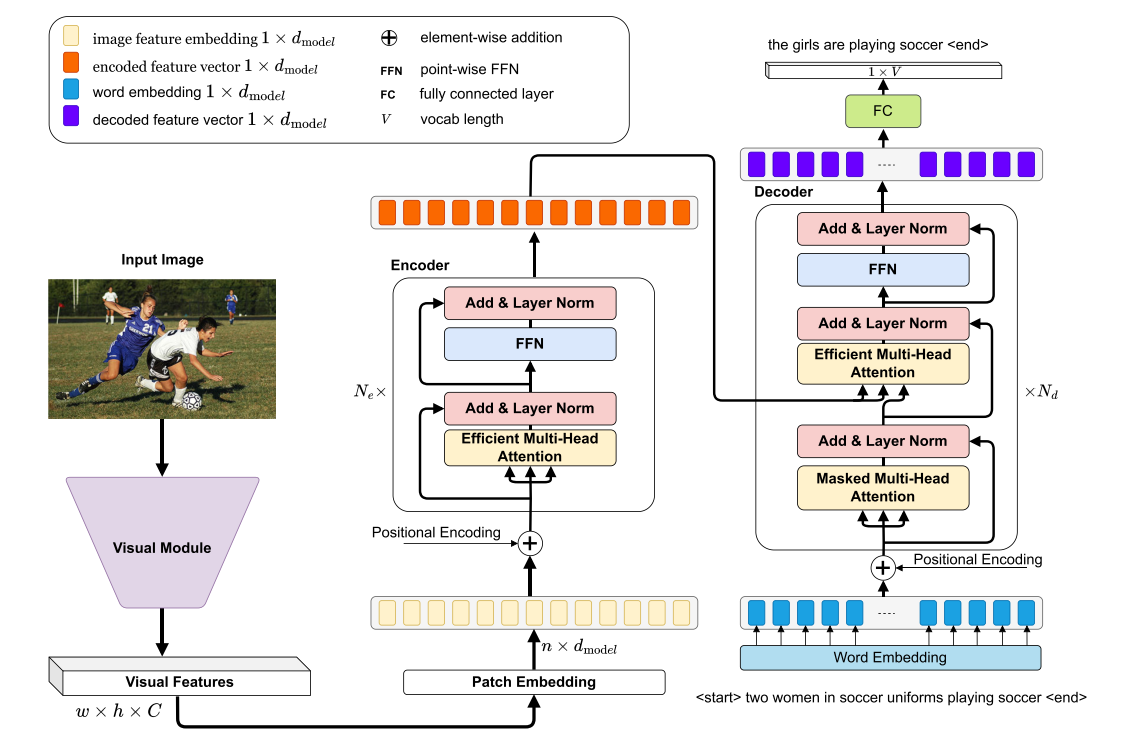 ETransCap: Efficient Transformer for Image CaptioningAlbert Mundu, Satish Kumar Singh, and Shiv Ram DubeyApplied Intelligence, Aug 2024
ETransCap: Efficient Transformer for Image CaptioningAlbert Mundu, Satish Kumar Singh, and Shiv Ram DubeyApplied Intelligence, Aug 2024Image captioning is a challenging task in computer vision that automatically generates a textual description of an image by integrating visual and linguistic information, as the generated captions must accurately describe the image’s content while also adhering to the conventions of natural language. We adopt the encoder-decoder framework employed by various CNN-RNN-based models for image captioning in the past few years. Recently, we observed that the CNN-Transformer-based models have achieved great success and surpassed traditional CNN-RNN-based models in the area. Many researchers have concentrated on Transformers, exploring and uncovering its vast possibilities. Unlike conventional CNN-RNN-based models in image captioning, transformer-based models have achieved notable success and offer the benefit of handling longer input sequences more efficiently. However, they are resource-intensive to train and deploy, particularly for large-scale tasks or for tasks that require real-time processing. In this work, we introduce a lightweight and efficient transformer-based model called the Efficient Transformer Captioner (ETransCap), which consumes fewer computation resources to generate captions. Our model operates in linear complexity and has been trained and tested on MS-COCO dataset. Comparisons with existing state-of-the-art models show that ETransCap achieves promising results. Our results support the potential of ETransCap as a good approach for image captioning tasks in real-time applications. Code for this project will be available at https://github.com/albertmundu/etranscap.
@article{Mundu2024, author = {Mundu, Albert and Singh, Satish Kumar and Dubey, Shiv Ram}, title = {ETransCap: Efficient Transformer for Image Captioning}, journal = {Applied Intelligence}, year = {2024}, month = aug, day = {27}, publisher = {Springer}, issn = {1573-7497}, doi = {10.1007/s10489-024-05739-w}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-024-05739-w}, }
2022
- CVIPScene Graph Generation with Geometric ContextVishal Kumar, Albert Mundu, and Satish Kumar SinghInternational Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing, Aug 2022
Scene Graph Generation has gained much attention in computer vision research with the growing demand in image understanding projects like visual question answering, image captioning, self-driving cars, crowd behavior analysis, activity recognition, and more. Scene graph, a visually grounded graphical structure of an image, immensely helps to simplify the image understanding tasks. In this work, we introduced a post-processing algorithm called Geometric Context to understand the visual scenes better geometrically. We use this post-processing algorithm to add and refine the geometric relationships between object pairs to a prior model. We exploit this context by calculating the direction and distance between object pairs. We use Knowledge Embedded Routing Network (KERN) as our baseline model, extend the work with our algorithm, and show comparable results on the recent state-of-the-art algorithms.
@article{10.1007/978-3-031-11346-8_30, title = {Scene Graph Generation with Geometric Context}, author = {Kumar, Vishal and Mundu, Albert and Kumar Singh, Satish}, journal = {International Conference on Computer Vision and Image Processing}, volume = {1567}, number = {5}, pages = {340--350}, year = {2022}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-11346-8_30}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-11346-8_30}, }
